October 25th, the 33th event of Academic series of Hujiang Economy & Management symposium of Business School was hosted at VOOV meeting (ID: 284-797-292), Zhang Xi, Ph.D in Department of Public Administration, presented “Provincial driving forces and pathway of achieving China’s CO2 emission-reduction targets” .
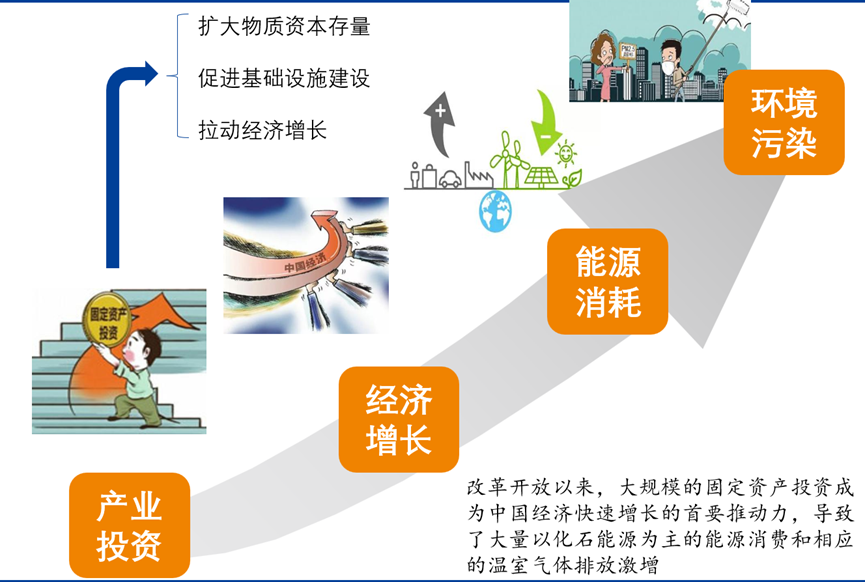
The signing of the Paris Agreement opens a new stage of global climate change governance. As the world’s largest carbon emitter, China is proactively taking responsibility for reducing emissions. The Chinese government has pledged to cut carbon emissions per unit of GDP by 60% to 65% from 2005 levels by 2030, with total emissions peaking around 2030. Due to China’s vast territory and uneven development, the national carbon reduction target cannot be achieved without the efforts of the provinces. In this context, exploring the driving factors and emission reduction paths of China’s provincial carbon emissions is particularly important to achieve the national carbon emission reduction target, which is an important topic to be explored. The report focuses on how to achieve China’s CO2 emission reduction targets through provincial efforts. First, the driving forces of national and provincial CO2 emissions from 1995 to 2016 are studied using a generalized Divisia index decomposition model with both traditional and investment factors. Second, Monte Carlo simulation technology is used to incorporate uncertainty into the investigation of the potential evolution path of CO2 emissions, and scenarios are used to analyze the future CO2 emissions of Chinese provinces under different development paths. Third, this study compares and analyzes the contribution of provincial factors to the national CO2 emission reduction target, and discusses how to formulate effective CO2 emission reduction policies at the provincial level.
After presentation, colleagues and students summarized theoretical contributions and practical implications of this study, and they also suggested further research direction and insightful comments.
Contributor: ZHANG Xi


